One step backward, Two steps forward.
Protected Mode:
=> Preparations:
Well for our operating system to make the switch from 16 bit to 32 bit we need to do some preparations, that involves saying good bye to the BIOS, setting up the GDT and making a lot of bugs while trying to make a driver for the keyboard.
=> GDT:
We used segmentation before in 16 bit mode, but here things work differently, in 32 bit we need to define The Global Descriptor Table(GDT), which is a structure where we define the descriptor of the segment we use, it's contains various properties and flags that define how and what our segment will do, will we be able to read it ? or to write to it ?...
=> GDT && Memory Models:
The GDT allow us to define and use different memory models from which:
- Flat memory model: This model uses physical addresses. In the flat memory model memory is viewed as a contiguous address space, starting from 0 and going up to the maximum address. Those addresses correspond directly to the physical locations of memory in the RAM, this makes memory access simple, but also makes implementing memory protection harder, cause all programs have equal access to the intire memory space.
- Segmentation: Here the memory is divided into smaller sections called segments. each of them can be assigned different access privileges. So segmentation provides a form of memory safety by allowing us to asign different access privilege (read-only for example) to each segment, but also add more overhead, as the processor must keep track of segment register values and switch between segments as needed.
- Paging: This is a more advenced form od memory management that devides memory into fixed-size pages (typically ranging from 4KB to 8KB in size), ad maps these pages to the virtual memory addresses used by the operating system and applications. This allows for more control over memory access and used to implement virtual memory, where a program can access a larger adress space than is physically available by temporarily swapping pages of memory from and to the disk.
So while paging offers the most protection, it's also a way more complexed than the flat memory model, while segmentation is between the two models, providing some protection while relatively simple to implement. In YonaOS we will go for the flat memory model for now, I do trust you, and your skills as a programmer, and provide you with the full privilege of the whole RAM.
=> How to define the GDT for The Flat Memory Model:
; The GDT must contain at least two segments:
- The code Segment.
- The Data Segmemt.
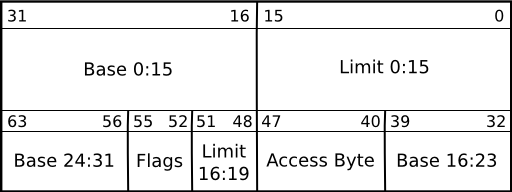
- Base Address (32 bit): The starting address of a segment.
- Limit (20 bits): The size of the segment.
- Access rights (8 bit): defines the access rights for the segment, such as read, write, and execute permissions.
- Flags (4 bits): additional flags that specify the properties of the segment.
; Define The GDT In Assembly:
Well understanding what a GDT is a thing and defining it is an other, well you can visit the source code in YonaOS and find out how wierd it's to declare it, for example instead of declaring the address base (32 bit), you need to define 16 bit from the limit (20 bit), then define 24 bit of the base, and it's a miss, I don't know why it should be like this a joke ? revenge ? who knows.
; The Structure To Define A Segment:
=> Switching to 32 bit mode:
After defining the GDT, the switch to 32 bit protected mode is straight forward. First we need to load the GDT we've constructed before with a special instruction called 'lgdt'. Then we will disable all interrupts with the instruction 'cli', and by that we will be done with the BIOS. After that we will set the first bit of a special control register cr0, to indicate that the CPU now is working in 32 bit mode.
Now all what we need to do is forcing the cpu to complete any instructions currently executed (pipeline issues) in the 16 bit mode (if there is any), to fully swich and be sure that everything is working in the right mode, we can do that by doing a far jump, which is like the standard jump but we add the target segment at the begining which will be the Code Segment for us, also updating our registers will be handy, as our old values for them are useless now.

